DDCCSD
This example uses the data-driven coupled-cluster singles and doubles (DDCCSD) model to predict energies along the dissociation curve of a water molecule. The DDCC method is presented in the publication Data-Driven Acceleration of the Coupled-Cluster Singles and Doubles Iterative Solver, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2019, 10, 4129. For exploration of locality, please see Transferable MP2-Based Machine Learning for Accurate Coupled-Cluster Energies, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2020, 16, 7453.
Link to the code repository: DDQC Demo
Required python3 modules:
- numpy
- psi4
- os
- sklearn
- matplotlib
If you are missing any of these packages, we would recommend using the following lines in your juypter notebook:
import sys
!{sys.executable} -m pip install missing_package_name
Import packages
# Import the packages
import psi4
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsRegressor
from helper_CC_ML_old import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
MLt2=0
# Below is a list of features utilized in the DDCCSD scheme
features = ['Evir1', 'Hvir1', 'Jvir1', 'Kvir1',
'Evir2', 'Hvir2', 'Jvir2', 'Kvir2',
'Eocc1', 'Jocc1', 'Kocc1', 'Hocc1',
'Eocc2', 'Jocc2', 'Kocc2', 'Hocc2',
'Jia1', 'Jia2', 'Kia1', 'Kia2',
'diag', 'orbdiff', 'doublecheck',
't2start', 't2mag', 't2sign',
'Jia1mag', 'Jia2mag', 'Kia1mag', 'Kia2mag']
'''
Key:
Letters:
E-Energy of the orbital
H-1e contribution to the orbital energy
J-Coulombic contribution to orbital energy
K-Exchange contribution to orbital energy
Placement: occ or virt
Number: is it electron one or two from the two electron excitation
Jia1- coulomb integral between orbital occ1 and vir1
Jia2 " but 2
Kia1 - exchange integral between orbital
Kia2 Same but exchange integral
diag - is it on the diagonal, aka, are the two excited electrons going to the same orbital **this is important fyi
orbdiff - (Evir2 + Evir1 - Eocc1 - Eocc2)
doublecheck - full 2electron integral
t2start - INITIAL MP2 amplitude **this is the inital guess
t2mag - np.log10(np.absolute(t2start)) ~ this is going to be a common trend, since it is more straightforward for ML algorithms to understand
t2sign - (t2start > 1)?
Jia1mag - np.log10(np.absolute(feature))
Jia2mag np.log10(np.absolute(feature))
Kia1mag np.log10(np.absolute(feature))
Kia2mag np.log10(np.absolute(feature))
'''
# These feature weights have been optimized through a gridsearch optimization
factors=(1,1.25,1.5,2,5,10,100,1000)
factor= np.zeros((len(features)))
finalfactor=factor
factor[2]=3
factor[6]=3
factor[12]=4
factor[8]=4
factor[16]=1
factor[17]=1
factor[20]=5
factor[21]=5
factor[22]=6
factor[23]=6
factor[24]=5
factor[25]=1
factor=factor.astype(int)
for j in range(0,len(features)):
a=factor[j]
finalfactor[j]=factors[a]
# This function extracts the features and the t2 amplitudes for the training set.
def GetAmps(Foldername, occ=False, vir=False):
i=1
for filename in os.listdir(str(Foldername)):
psi4.core.clean()
file_path=str(str(Foldername)+filename)
text = open(file_path, 'r').read()
mol = psi4.geometry(text)
psi4.core.clean()
psi4.set_options({'basis': 'cc-pVDZ',#'6-31g',
'scf_type': 'pk',
'reference': 'rhf',
'mp2_type': 'conv',
'e_convergence': 1e-8,
'd_convergence': 1e-8})
A=HelperCCEnergy(mol)
A.compute_energy()
matrixsize=A.nocc*A.nocc*A.nvirt*A.nvirt
Bigmatrix=np.zeros([matrixsize, len(features)])
for x in range(0,len(features)):
Bigmatrix[:, x]=getattr(A, features[x]).reshape(matrixsize)
Bigamp=A.t2.reshape(matrixsize,1)
if i==1:
Bigfeatures=Bigmatrix
Bigamps=Bigamp
i=2
else:
Bigfeatures=np.vstack((Bigfeatures,Bigmatrix))
Bigamps=np.vstack((Bigamps,Bigamp))
array=Bigfeatures
finalamps=Bigamps
return array,finalamps
Error Calculation
- Error is calculated using following equation:
- Start Energy = Energy calculated by substituting the predicted \(t_{2}\) amplitude to CCSD energy equation
- Final Energy = Energy calculated by substituting the optimized \(t_{2}\) amplitude to CCSD energy equation
# This function retrives the features for the test set and then predicts the t2 amplitudes.
# The predicted amplitudes are then passed back to Psi4 for the CCSD energy to be iteratively optimized.
def Test(Foldername, occ=False, vir=False):
steps=list()
difference=list()
supalist=list()
startenergy=list()
finalenergy=list()
filenames=list()
rhfenergy=list()
OH_distance_list = list()
for filename in os.listdir(Foldername):
psi4.core.clean()
filenames.append(filename)
print ("filename is "+filename)
file_path=str(Foldername+filename)
xyz_file = open(file_path, 'r')
text = xyz_file.read()
xyz_file.close()
xyz_file = open(file_path, 'r')
text_lines = xyz_file.readlines()
xyz_file.close()
print(file_path)
mol = psi4.geometry(text)
psi4.set_options({'basis': 'cc-pVDZ',
'scf_type': 'pk',
'maxiter': 1000,
'reference': 'rhf',
'mp2_type': 'conv',
'e_convergence': 1e-8,
'd_convergence': 1e-8})
MLt2=0
A=HelperCCEnergy(mol)
matrixsize=A.nocc*A.nocc*A.nvirt*A.nvirt
Xnew=np.zeros([1,matrixsize,len(features)])
for x in range (0,len(features)):
Xnew[0,:,x]=getattr(A, features[x]).reshape(matrixsize)
Xnew=np.reshape(Xnew, (matrixsize,len(features)))
X_new_scaled= scaler.transform(Xnew)
X_newer_scaled= X_new_scaled
for x in range (0,len(features)):
X_newer_scaled[:,x] *= finalfactor[x]
ynew2=knn.predict(X_newer_scaled)
MLt2=ynew2.reshape(A.nocc,A.nocc,A.nvirt,A.nvirt)
A.t2=MLt2
OH_distance = float(text_lines[1].split()[2])
A.compute_t1()
A.compute_energy()
rhfenergy.append(A.rhf_e)
startenergy.append(A.StartEnergy)
finalenergy.append(A.FinalEnergy)
OH_distance_list.append(OH_distance)
startEn = np.add(np.array(startenergy),np.array(rhfenergy))
finalEn = np.add(np.array(finalenergy),np.array(rhfenergy))
difference.append(sum( np.abs(np.asarray(startenergy) - np.asarray(finalenergy))) /len(startenergy))
differences = np.abs(np.asarray(startenergy) - np.asarray(finalenergy))
print('-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------')
print ('Average Error: ')
print (difference)
return(startEn, finalEn, OH_distance_list)
# Extract training features (X_train) and amplitudes (y_train)
X_train,y_train=GetAmps('Water/Regular/Water5/')
# Scale the features using a MinMaxScaler in Scikit-Learn
scaler = MinMaxScaler().fit(X_train)
X_train_scaled = scaler.transform(X_train)
# Multiply the features by the optimized weights
for a in range(0,len(features)):
X_train_scaled[:,a] *= finalfactor[a]
# Train the regression model
knn=(KNeighborsRegressor(n_neighbors=1, p=2).fit(X_train_scaled,y_train) )
# Calls the Test function described above, which returns the start energy, the final, or optimized, energy, and the OH radius
startEnergy, finalEnergy, OH_distance = Test('Water/Water100/')
# Plot the start energy and final energy against bond distance
zipped_lists = zip(OH_distance, startEnergy, finalEnergy)
sorted_pairs = sorted(zipped_lists)
tuples = zip(*sorted_pairs)
BondDistance, StartEnergy, FinalEnergy = [ list(tuple) for tuple in tuples]
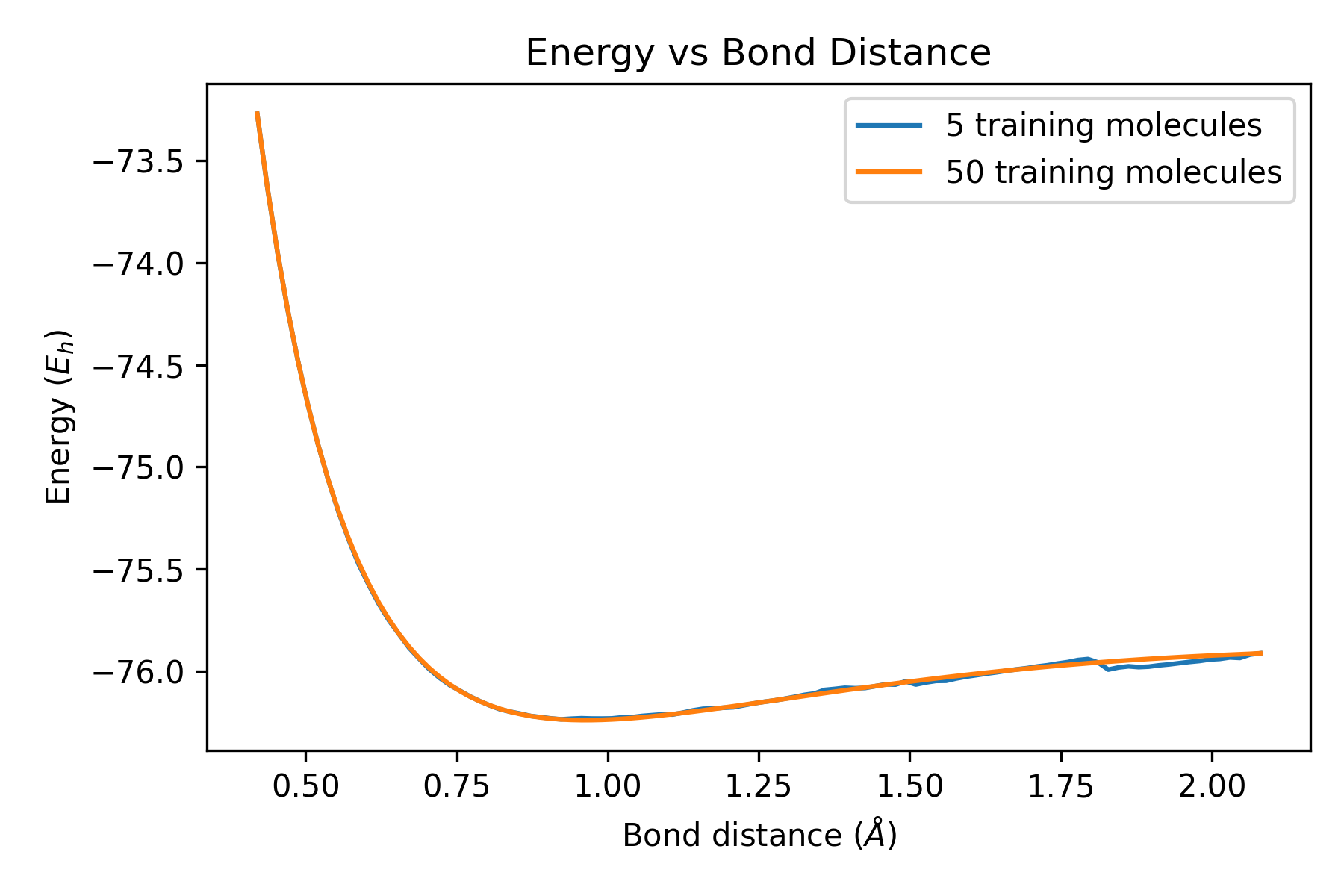
plt.title('Energy vs Bond Distance')
plt.xlabel('Bond distance ($\AA$)')
plt.ylabel('Energy ($E_{h}$)')
plt.plot(BondDistance, StartEnergy, label = '5 training molecules')
plt.plot(BondDistance, FinalEnergy, label = '50 training molecules')
plt.legend(loc="upper right")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('new_Varuna_figure.png',dpi=300)
plt.show()